- tecnotales.com
- September 23, 2024
- 0 Comments
5G vs 4G: The Future of Connectivity Unveiled
Technology is ever pervading and one of the most recent discoveries is the emergence of 5G technology in the market. As the next step in the technological evolution of the wireless communication with even higher speeds, lower latency and increased connectivity 5G is about to transform the manner of the digital interaction. But how many of those deccelerations were there and how does it compare to its immediate predecessor 4G? In this blog, we are going to look at what distinguishes 5G vs 4G in terms of efficiency, advantage, disadvantage and what the next generation of connectivity might bring after 5G.
Understanding 4G: The Foundation of Modern Connectivity
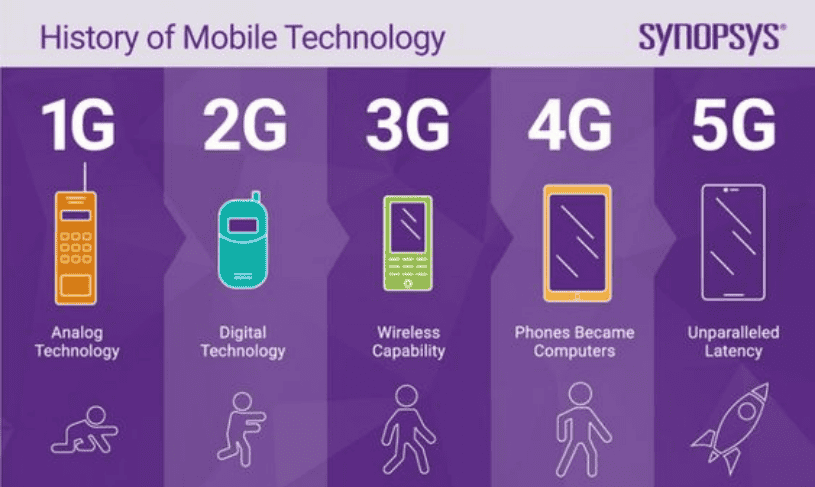
The following section gives an insight of the duties that 4G offered in cultivating today’s environment of mobile technology before exploring the new capacities of 5G. Launched in the late 2000s as an upgrade from the 3G, 4G LTE (Long Term Evolution) offered better data speeds, network dependability and improved mobile internet experience.
Speed and Performance
The major development that came with 4G was on the speed.. Where 3G networks offered still a good enough throughputs of up to 3 Mbps in download, 4G LTE could go up to theoretical throughputs of up to 150 Mbps. This additional speed made it possible to stream high-definition videos and movies without interruption, facilitate easier and faster browsing of the Internet as well as enable provision of reliable connection to applications and services.
Improved Latency
Another concern that 4G provided an enhanced solution was the issue of latency which is defined as the time taken between data transmission and data reception. When the service providers begun offering 4G services the latency was at 30-50 ms compared to the 100-200 ms of 3G services. This decrease in latency played a important role in making the usage of application and services that need real-time interaction such as video calling, or online gaming, a more streamlined experience.
Increased Network Capacity
Where as 4G network was developed to carry a larger amount of data traffic due to the increasing mobile devices and inundation of data centric applications. These improvements contributed to the growth of mobile applications, social networks, and streaming, which appeared to be mainstream in the second half of the 2010s.
Enter 5G: A New Era of Connectivity
As the advances of technology went on, the effects of the limitations within 4G were showing and this is how the need for a new generation of wireless technology came. That is where 5G comes into play. 5G which came into the market in the early 2020s is even faster, has even lower latency and even more reliable than the previous generations.
Speed and Performance
It opens the prospects of almost infinite speed connection. While the 4G LTE networks provide a optimum speed to the tune of 150 Mbps, the 5G networks have the potential speed of up to 10 Gbps. This leap in performance as will result in ultra-high-definition video streaming, faster downloads and efficient data management.
Ultra-Low Latency
What 5G does is that it takes latency reduction to a whole new level. As we have seen above theoretical latencies as low as 1 millisecond meaning response for applications and services are almost instantaneous. This ultra-low latency is especially important for a number of modern applications that imply real time interaction, including self-driving cars, telesurgery, or next generation gaming.
Enhanced Network Capacity
5G networks are planned with higher density of connections and data traffic as compared to the 4G networks. This higher capacity is needed especially as the total of connected devices remains to rise due to the growing Internet of Things (IoT) or smart devices market. An increased network capacity of 5G will mean that the overloaded places like cities or large events will also be easy to navigate.
Key Differences Between 5G and 4G
While both enhancements will seek to boost connectivity, the divergence between the two could not be deeper. Here’s a breakdown of the key areas where 5G surpasses 4G:
Speed
5G: Up to 10 Gbps - 4G: Up to 150 Mbps
The distance improves extremely when using the 5G as compared to the 4G system. Although 4G offered a greatly enhanced performance compared to 3G system; the relative speeds in which 5G can offer is many orders of magnitude better. This will allow for entirely new use cases and applications which were not feasibly possible with the previous 4G network.
Latency
5G: As low as 1 millisecond - 4G: 30-50 milliseconds
From the issue of latency, it is clear that 5G has been important in cutting down the latency which is important for real-time applications. This ultra-low latency will improve experiences in aspects such as virtual reality, the remote control of heavy machinery or vehicles, and auto-mobiles.
Network Capacity
5G: Designed to handle up to 1 million devices per square kilometer
4G: Designed to handle thousands of devices per square kilometer
The proposed 5G must support much more devices per a square kilometer as the number of the connected devices increases and the demand for data as well. With enhanced capacity of this nature, the network performance is expected to remain steady and not deteriorate wherever there is high density.
Coverage and Frequencies
5G: Utilizes a wide range of frequencies, including high-frequency millimeter waves
4G: Primarily operates on lower-frequency bands
This made 5G to offer operations with cellular speeds and other improved operation capacity as compared to 4G but it depends on the use of millimeter waves making it require many base stations and a short range compared to the lower bands. This means that although 5G can provide enhanced performance, the availability of the said technology is likely to be constrained at the beginning.
The Benefits of 5G
It is also true that the advancement from 4G to the still relatively new 5G does not only offer a faster connection to the Internet, but a lot of other advantages as well. Here are some of the key advantages of 5G technology:
Enhanced Mobile Experience
This is because 5G will offer improved speed and minimized latency hence resulting in enhanced mobile experience. The following are the benefits that the users are likely to enjoy: High Quality Service, Streaming of High Definition videos, Minimal Buffering time, Fast download of big files, Real-time interactions with other users.
Support for Emerging Technologies
All these applications are expected to be enabled by the 5G network enabling applications such as autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and advanced robotics. Its low latency and the high amount of available capacity make it suitable for these innovations and open the door to new use cases and applications that were not possible with the 4G.
Improved Connectivity for IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) which is simply an extension of the internet to a larger number of devices is going to grow fabulously with the help of 5G. The connectivity of such a large number of devices through the technology will foster smart homes, industrial operations and hence, the IoT applications. This increased connectivity will enhance the quality of life in the following ways and will drive efficiencies through;
Economic Growth
5G is also anticipated to stimulate the economy through the generation of demand for its commercial applications and spin off on new ventures. Healthcare, transportation and manufacturing are some of the beneficiaries in the fifth generation telecoms technology through enhanced features leading to production optimization and additional sources of income.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its many advantages, 5G also faces several challenges that need to resolve as the technology continues to roll out:
Infrastructure Requirements
The introduction of 5G brings considerable expenditure to modern telecommunications networks, for instance’distribution centers of base stations and network components. This often proves to be an obstacle in the expansion of coverage area, especially, in the areas with quantitative features, or rather, with quantitative values when the improvement of coverage area is a problem with constraints, such as, for example, the absence or shortage of capital, difficult absolutely or relatively terrain, etc.
Coverage Limitations
Newer even though 5G is better in performance issues it may initially have a restricted coverage area than 4G. Unlike 4G networks which employ relatively low frequency K/KA bands that are able to cover large areas with low power, 5G networks will have to use more power of the higher frequency millimeter waves that are able to provide high speed but low range and therefore might require more base stations to provide adequate coverage.
Cost and Accessibility
Some of the drawbacks of 5G technology include a high cost of adopting this technology and differences in availability across the regions. Another challenge that is likely to arise in the future is making beneficiaries of 5G users across the board irrespective of the demographic status of the area in question.
Security and Privacy
Like with any other new generation of network technology, 5G create new security and privacy challenges. Implementing preventive measures against threats that may affect the networks and those devices will be significant in preserving the users’ trust and protecting their data.
The Future of Connectivity
Looking at the future shift of 4G to 5G can consider as a giant leap in providing the internet connection. These capabilities mean that the application of 5G will create new opportunity and spur new developments in numerous sectors. Being the next generation of communications, 5G faces its share of hurdles but promises great returns and a revolutionary change in the way the Internet is.
To sum up, it is possible to mention that the transition from the 4G to the 5G network is quite an exciting step in the sphere of connection. Given its great potential for the future of technology and people’s interaction with it, 5G technology has great potential as it gradually develops. In terms of application enablement, support for new solutions, or economic development, 5G will prepare the society for what is possible in the context of digital transformation.